Bitfields
Bitfields are collections of booleans
boolean values (true/false, 0/1, yes/no) are each exactly 1 bit. For efficiency, they can be packed together tightly into special Vectors or Lists called Bitfields
Bitvector / Bitlist
-
A Bitvector is a Vector of boolean values, with a fixed size of N
-
A Bitlist is a List of boolean values, with a limit of N
- While these could be treated as
Vector[boolean, N] and List[boolean, N], SSZ offers a more efficient method for serializing bitfields
Bitvector
-
Type:
-
Default value:
-
Illegal type:
Bitvector[0] is an illegal type, since fixed-length types many not have 0 byte-length representations
-
Serialization:
- A fixed-length sequence of
N bits, packed into (N + 7) // 8 bytes.
- a bit at sequence index
i is put into byte i // 8 and matches 1 << (i % 8) within that byte
- If
N is not a multiple of 8, the last byte is packed with zeroes
-
Merkleization
- A bitvector is merkleized by serializing it, and then merkleizing it as a
Vector[byte, ((N + 7) // 8)]
Bitlist
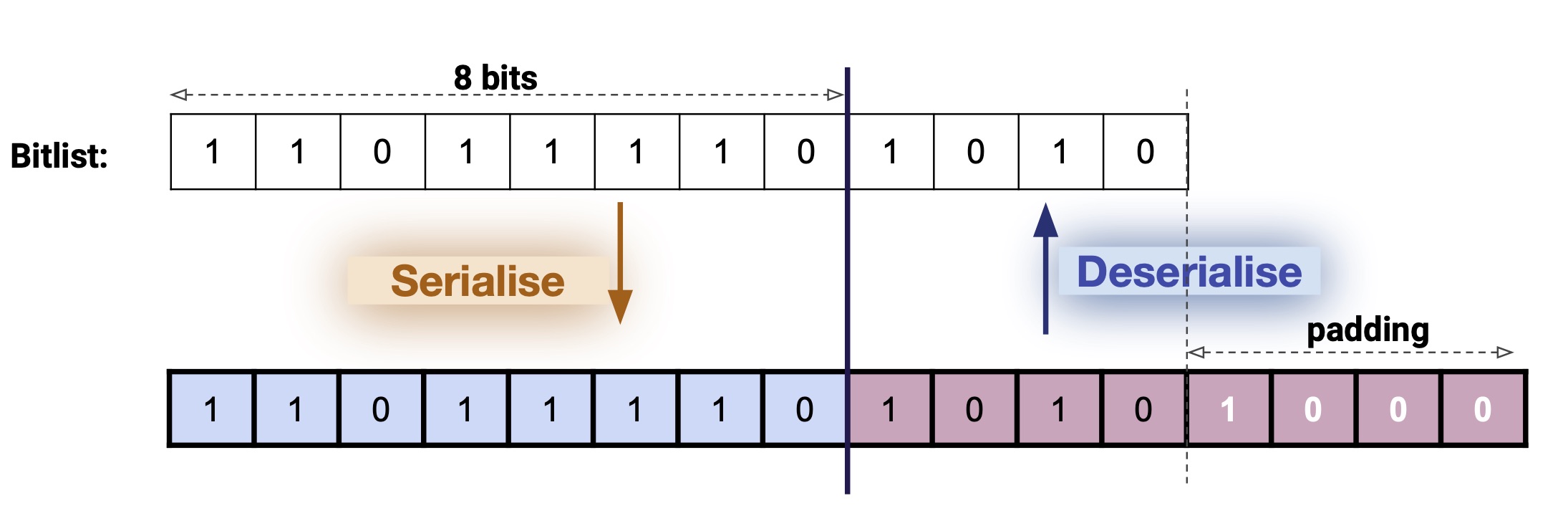
A bitlist is a dynamic-length sequence, with a limit of N bits, packed into bytes.
-
Type:
-
Default value**:
0 bits, i.e. an empty bitlist
-
Serialization
- a bit at sequence index
i is put into byte i // 8 and matches 1 << (i % 8) within that byte
- From the offset coding, the length (in bytes) of the bitlist is known. An additional 1 bit is added to the end, at index e, where e is the length of the bitlist (not the limit), so that the length in bits will also be known
- This delimiting
1 bit is put in what would effectively be the bitfield index bit_length(bitlist_value).
- Note that for an empty bitlist that would be the first bit at index 0: A single zeroed byte, or empty bytes, is illegal as bitlist representation.
-
Size:
- Because of this delimiting bit, the total byte length for serialization purposes is:
(((N + 1) + 7) // 8) == ((N // 8) + 1)
-
Merkleization
- For merkleization, the length of the bitlist is mixed in with the root, and hence the delimiting bit is not used for merkleization.
- Similarly to a
List, the subtree is padded to fit the limit of the bitlist.